Neurocysticercosis is an intracranial parasitic disease. This is due to the pork tapeworm larvae, Taenia solium. Many developing countries consider this disease a significant public health issue, and cases have also been reported in developed countries due to travel or migration. It is equally important for a neurologist to explain neurocysticercosis in terms of its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, treatment and management.
What is Neurocysticercosis
Neurocysticercosis results when the larvae of Taenia solium penetrate the brain tissue to give rise to several neurological manifestations. These larvae can encyst in various regions of the brain; therefore, their number, size, and location cause different symptoms.
Causes of Neurocysticercosis
Neurocysticercosis is mainly acquired through the ingestion of T. solium eggs from food or water. Some of the most critical risk factors include poor sanitation and hygiene. This is how the infection cycle generally goes
- Infection People take foods or water containing eggs of the pork tapeworm.
- Release The eggs hatch in the intestines and release larvae.
- Larvae Migration These larvae move through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream and move to the brain, muscles, and other organs.
- Larvae Development in the brain, and the larvae form cysts which leads to neurocysticercosis.
Symptoms of Neurocysticercosis
Neurocysticercosis is characterized by various signs and symptoms depending on the number of cysts and their location in the brain. Common symptoms include
- Seizures are the most common manifestation, they may be the only initial symptom of the disease.
- Headaches Other symptoms include persistent and severe headaches resulting from raised intracranial pressure.
- Neurological Deficits These may include weakness, numbness, or vision problems.
- Cognitive Impairment Memory loss, and difficulty concentrating are possible.
- Hydrocephalus Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain due to the presence of excessive amounts of cerebrospinal fluid.
Diagnosis of Neurocysticercosis
The neurocysticercosis diagnostic approach includes clinical assessment, imaging, and lab tests.
- Clinical assessment is actively performed on patients by interviewing them and conducting a physical examination, which is one of the assessment techniques used in patient evaluation.
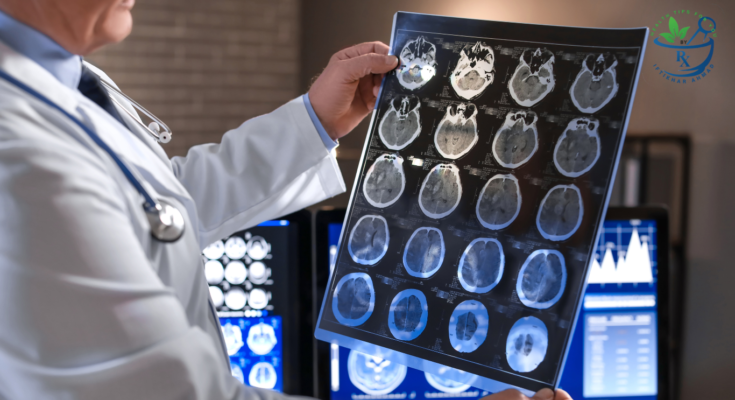
- Neuroimaging techniques like MRI and CT scans help depict cysts in the brain. These images can depict an area’s density, size, and position related to cysts and possible inflammation or oedema.
- In this case, the serological tests facilitate in diagnosing Taenia solium by detecting antibodies in the blood samples. The two most commonly used tests include the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and the enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot (EITB).
- Discover neurocysticercosis: its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Stay informed about this serious parasitic brain infection.
Prevention of Neurocysticercosis
To control new cases of neurocysticercosis, there is a need to enhance personal hygiene and sanitation standards. Below are some of the best-prevented measures
- Hand hygiene: Wash your hands with soap and water, and clean and wash your hands before eating, after using the toilet, and any other time your hands get dirty.
- Water Safety The importance of drinkable water, free from contaminants. Safe water practices; for example, boiling or treating water if the safety of the water is in doubt.
- Personal hygiene Washing of hands and bodies, and handling of food and domestic animals in a hygienic manner.
- Health educators not only educate people on how they can contract Taenia solium, but also provide them with the necessary information to prevent infection. Furthermore, they offer practical steps that individuals can take to avoid getting infected, thereby promoting a healthier and more informed population.
Treatment and Management of Neurocysticercosis
The effective management of neurocysticercosis involves a multi-faceted approach, which begins with identifying the parasites, followed by controlling their growth and subsequently addressing the clinical manifestations and potential complications. Additionally, this comprehensive strategy ensures that all aspects of the condition are adequately managed.
Antiparasitic Therapy
- Albendazole, a first-generation antiparasitic drug, is used to treat several kinds of worm infections and is particularly efficient in the treatment of the larval stage of the tapeworm.
- Praziquantel is another antiparasitic drug that can be used as a single drug or mixed with Albendazole.
Anti-inflammatory Therapy
Corticosteroids like dexamethasone or prednisone are used to actively decrease inflammation and prevent reactions that may occur when the larvae die.
Symptomatic Treatment
- Used in the management of seizures which is a symptom that is recurrent in many patients. Doctors frequently administer drugs such as phenytoin, carbamazepine or levetiracetam as antiepileptic agents.
- In addition to Pain Management Analgesics, these medications encompass a range of treatments that specifically target headaches and other types of pain, thereby providing comprehensive relief.
Surgical Intervention
Sometimes, the operation may be necessary for the excision of large cysts or in case of raised intracranial pressure due to hydrocephalus. Surgical options include
- Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting To relieve pressure and drain cerebrospinal fluid.
- Surgical intervention Surgical excision of cysts although this is rare and depends on the size and location of the cysts.
Long-term Management
Long-term outcomes of neurocysticercosis involve closely following for relapse, chronic manifestations of the disease, as well as commitment to protective measures. Healthcare providers recommend continued visits.
Conclusion
Healthcare providers should diagnose and treat neurocysticercosis, a significant parasitic disease, as soon as possible. By actively understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and implementing prevention measures, individuals can effectively mitigate the consequences of this illness. Furthermore, taking these proactive steps will significantly reduce the impact and severity of this sickness. However, due to better medical facilities and awareness, the management of neurocysticercosis has improved and hence there is hope for those affected by this condition. Moreover discover neurocysticercosis: its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Additionally, stay informed about this serious parasitic brain infection.
References
- Garcia, H. H., & Del Brutto, O. H. (2005). Neurocysticercosis updated concepts about an old disease. The Lancet Neurology, 4(10), 653-661.
- White, A. C., Coyle, C. M., & Rajshekhar, V. (2018). Diagnosis and treatment of neurocysticercosis. Nature Reviews Neurology, 14(7), 416-426.
- Nash, T. E., & Garcia, H. H. (2011). Diagnosis and treatment of neurocysticercosis. Nature Reviews Neurology, 7(10), 584-594.
- Pal, D. K., & Carpio, A. (2010). Neurocysticercosis clinical management and treatment. Lancet Neurology, 9(5), 475-487.
- Carpio, A., & Kelvin, E. A. (2011). The treatment of epilepsy in neurocysticercosis a systematic review. The International Journal of Medical Reviews, 92(1), 2-9.